하인두에 발생한 점막 연관성 림프조직 림프종 1예: 증례 보고
A Case of Mucosa-Associated Lymphoid Tissue Lymphoma (MALT Lymphoma) in Hypopharynx: A Case Report
Article information
Abstract
= Abstract =
Malignant lymphoma rarely occurs in the larynx and hypopharynx. Few cases of malignant lymphoma in the larynx were reported in Korea. However, malignant lymphoma in the hypopharynx had been not reported in Korea. A 68-year-old woman came to the outpatient clinic with a foreign body sensation in her throat. A round, smooth margin, bright pink-colored mass was confirmed by the laryngoscopy. The patient took neck computer tomography. A small bulging of mucosa was observed, but there was no peripheral infiltration or abnormally enlarged lymph nodes. We did excision using CO2 LASER. She was finally diagnosed with mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma (MALT lymphoma). After diagnosis, several image studies confirmed that there was no metastatic lesion. She got only radiotherapy after that and kept a complete response state for over 2 years.
서론
두경부에서 가장 흔한 악성 종양은 편평 세포암이지만, 악성 림프종도 종종 두경부 영역에서 발생한다.1) 악성 림프종은 호지킨 림프종과 비호지킨 림프종으로 나누어 지는데, 이 중 비호지킨 림프종이 더 흔하며, 두경부에서 발생하는 악성 종양의 대략 5% 정도를 차지한다.2) 호지킨 림프종은 주로 경부와 종격동의 림프절에서 발생하며, 림프절 외 부위에서는 5% 정도에서만 발생하는데 반해, 비호지킨 림프종은 림프절 외 부위에서도 30% 정도가 발생하고, 두경부에서는 침샘, 부비동, 발다이어 편도 고리 등에서 주로 발생하고 그 종류는 미만성거대 B세포림프종이 제일 흔하다.3,4) 반면 하인두 및 후두에서는 상대적으로 림프종의 발생이 낮다. 국내에서는 후두에서 발생한 악성림프종이 보고된 적은 있으나,5) 하인두에서 발생한 악성림프종은 아직 보고된 바가 없다. 특히 하인두에서만 원발성으로 발생한 점막 연관성 림프조직 림프종은 세계적으로도 매우 드물다.6,7) 저자들은 68세 여성에서 하인두에서 발생한 점막 연관성 림프조직 림프종 증례를 경험하여 보고하는 바이다.
증례
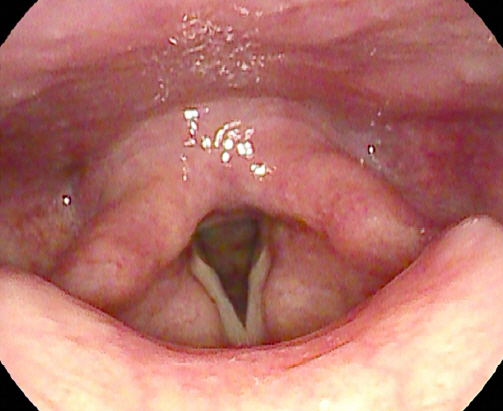
68세 여자 환자가 한 달 전부터 발생한 목 이물감 주소로 외래 내원하였다. 흡연 및 음주력은 없었으며, 과거력상 좌측 유방암으로 2009년도 11월 좌측 유방 절제술 및 보조항암화학요법 시행 받은 경험은 있으나 그 외 가족력 및 기타 이상 소견은 없었다. 환자는 가래, 목 이물감 외 목통증이나 연하 장애, 발성 장애 같은 증상들은 호소하지 않았다. 외래에서 시행한 후두 내시경 상 좌측 하인두 후벽에서 기원하는 표면이 부드럽고, 타원형이며 주변 점막과 비슷한 분홍 빛깔의 종물이 관찰되었다(Fig. 1). 양측 성대 움직임은 정상이었다. 경부 전산화단층촬영에서 좌측 하인두에 점막 경계를 따라 경미하게 조영증강이 되는 병변은 있었으나 명확한 종괴는 확인되지 않았고, 주변 연부조직 침윤 및 비정상으로 보이는 임파선 비대는 보이지 않았다(Fig. 2). 이 후 환자는 전신 마취 하에 CO2 LASER를 이용하여 절제하였다. 병변의 크기는 11x4x15 mm였다. 병리학적 소견상 광범위한 림프상피상 병변이 확인되었으며, 고배율 소견에서는 비전형적인 림프세포 침윤이 확인되었으며, 또한 풍부한 세포질과 과염색성 핵을 가진 형질 세포가 변연부에서 관찰되었다. 추가 면역염색에서 CD 20에 양성 소견 보이는 점막 연관성 림프조직 림프종으로 진단되었다(Fig. 3). 이후 환자는 전이 유무를 확인하기 위해 골수 검사, 폐, 복부-골반 전산화단층촬영, 양성자 단층 촬영 등을 시행하였으며, 전이 소견은 확인되지 않았다. 이후 환자는 방사선 단독 치료 시행하기로 결정되어, 23일동안 180cGy 선량으로 17번, 총 3,060cGy 해당하는 방사선 치료를 하인두 원발부위에 받았으며, 2년이 지난 지금까지 후두 내시경 및 전산화단층촬영 등 이미지 검사 상 완전 관해 상태를 유지하며 외래 추적 관찰 중이다(Fig. 4).
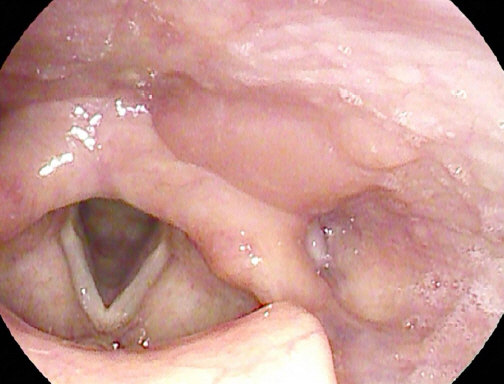
A laryngoscopic finding of mass in the hypopharynx. A round, smooth margin, bright pink-colored mass is observed via laryngoscopy on the left posterior wall of hypopharynx.
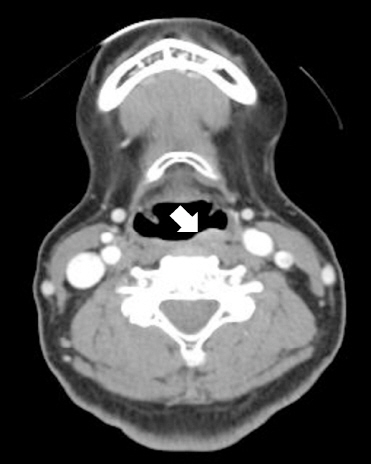
Computed tomography (CT) image of the mass in the hypopharynx. CT image shows the mild bulging contour at the left posterior wall of hypopharynx. The margin of lesion is a little enhanced, but there was no peripheral infiltration or abnormally enlarged lymph nodes.
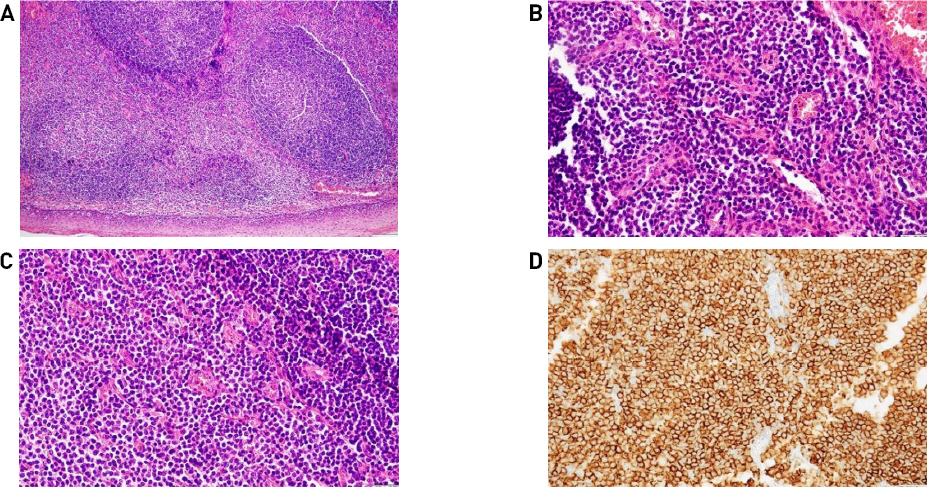
Histopathological findings of Mucosa-Associated Lymphoid Tissue lymphoma (MALT lymphoma) in the hypopharynx. (A) Diffuse lymphoid follicular cell proliferation is shown. (Hematoxylin & Eosin, x 100). (B, C) Infiltration of epithelial structures by lymphoid cells (Lymphoepithelial lesion) is shown. Plasma cells with abundant cytoplasm and hyperchromatic nuclei are shown in the marginal zone (Hematoxylin & Eosin, x 400). (D) Immuno-histochemistric finding is shown positive in CD 20 stain.
고찰
WHO 분류에 따르면 변연부 B세포 림프종(Marginal Zone B cell lymphoma, MZL)은 점막 연관성 림프조직 및 림프절 외 변연부 B세포 림프종(Extranodal MZL or MALT lymphoma), 비장 변연부 B세포 림프종(Splenic MZL), 림프절 변연부 B세포 림프종(Nodal MZL) 등 3가지로 분류할 수 있다. 점막 연관성 림프조직 림프종은 1983년 Isaacson과 Wright에 의해 처음 기술되었으며,8) 림프절 외 B세포 비호지킨 림프종의 하나로, 주로 위에서 발생하지만 침샘, 결막, 안와, 후두, 폐, 유방, 신장, 간 등 다양한 조직에서 발생할 수 있으며, 두경부에서 발생하는 비호지킨 림프종의 7-9%에 해당하고 다른 비호지킨 림프종과 달리 여성에서 유병률이 더 높다.9) 2017 WHO에 따르면 진단을 위해서는 조직검사가 필수이다. 점막 연관성 림프조직 림프종의 전형적인 특징 중 하나로, 중심구 유사(centrocyte-like) 변연부 B세포는 중소 크기의 약간 불규칙한 핵을 가지고 있으며, 핵소체는 눈에 띄지 않고, 염색질은 적당히 분산되어 있고, 세포질은 옅은 색을 띄고 있다. 다른 종류의 림프종과 감별을 위해 면역 염색을 하는데, 그 종류로는 주로 CD20, CD10, CD5, CD23, Cyclini D1, 면역글로불린 D (IgD), 및 SOX-1 등이 있다.10) 본 증례의 경우 비전형적인 림프세포 침윤이 확인되었으며, 면역 염색상 CD20 양성, CD3 음성, Ki-67 3% 결과 나와 변연부 B세포 림프종, 즉 점막 연관성 림프조직 림프종으로 진단되었다.
하인두에서 진단된 점막 연관성 림프조직 림프종의 내시경적 특징은 아직까지 보고된 바 없다. 본 증례의 경우 표면이 부드럽고, 타원형이며, 주변 점막과 비슷한 조직으로 덮인 종괴가 확인되었다. 점막 연관성 림프조직 림프종이 가장 호발하는 부위인 위에서 내시경 소견은 불규칙한 모양의 표재성 미란, 궤양, 확대된 주름, 두꺼워진 위벽까지 다양하게 보고되고 있다.11)
치료는 위말트림프종(Gastric MALT lymphoma)의 경우 Helicobacter pylori 제균 치료를 초치료로 시행하나, 위말트림프종이 아닌 경우 제균 치료는 권유되지 않는다.10) 치료 방법은 병기에 따라 결정되는데, 대다수를 차지하는 1, 2기는 제한된 병기로, 국소 치료 또는 전신 치료를 시행한다.10,12) 국소 치료는 수술과 방사선 치료로 나눌 수 있는데, 수술은 완전 절제가 가능하고, 수술 후 생활에 영향을 주지 않을 정도의 범위인 경우에는 효과적으로 보고되고 있으나, 수술의 범위가 광범위할 경우에는 수술적 절제에 있어 보다 더 신중한 결정을 요한다.10,13) 방사선 치료는 특히 위말트림프종 외 발생한 점막 연관성 림프조직 림프종의 1차 치료로 잘 알려져 있으며 보통 25-30Gy를 10-15번에 나누어 조사한다.14) 전신항암치료나 면역치료는 잘 시행되지 않으며, 방사선 치료에 금기에 해당하거나, 방사선 치료에 실패하였을 때 등 국한된 경우에 시도해 볼 수 있다.10,15) 본 증례의 경우 수술을 통해 점막 연관성 림프조직 림프종으로 진단이 되었으며, 수술 후 단일 부위에 발생한 점막 연관성 림프조직 림프종이 확인되어 치료로 3,060cGy 선량의 국소 방사선 치료를 시행하고, 이후 2년 넘게 완전 관해 상태를 유지하고 있다.
국내에는 아직 보고되지 않은 하인두에 발생한 점막 연관성 림프조직 림프종의 진단 및 치료를 경험하여 이를 보고하는 바이다.