구강내 절개로 제거한 협부 모기질종 1예
A Case of Buccal Pilomatricoma Removed Through Intraoral Incision
Article information
Abstract
= Abstract =
Pilomatricoma(or calcifying epithelioma) is a not common benign solitary tumor originated from outer root sheath cell of hair follicle or hair follicle of sebaceous glands. The tumor usually presents as an asymptomatic, hard, superficial located, and skin colored to reddish blue cutaneous mass. Most of the tumors are less than 10mm in diameter and adherent to the skin. Recently, 48-year-old man presented with cheek mass. The tumor was 2.6cm sized and located at the subcutaneous layer of cheek on CT scan. The tumor was clearly removed via transoral approach with buccal incision leaving no wound on face. The mass was confirmed as pilomatricoma on pathologic examination. Herein, we report our experience with literature review.
서론
1880년 Malherbe, Chenantais에 의해 처음으로 보고된 모기질종은 모낭 기질에서 기원하는 드문 양성 종양으로 주로 20세 이하, 특히 소아에서 많이 나타나며, 대개 두경부에서 발생하나 드물게 상지나 다른 여러 부위에서도 발생한다.1-4) 종물을 덮고 있는 피부와는 유착되어 있으나 주위 조직과는 경계가 명확한 고립성의 단단한 피하결절의 형태를 띈다.2-5) 대부분 통증이나 압통을 동반하지 않아 우연히 발견되는 경우가 많고 크기는 직경 1cm 내외로 매우 느리게 자라는 것으로 알려져 있다.3-6) 외과적 완전 절제가 치료법이며 불완전한 절제 시 드물게 재발할 수 있다.2,3)
최근 저자들은 우측 뺨에 발생한 모기질종을 구강 내 접근을 통해 안면부 흉터를 남기지 않고 절제한 증례에 대하여 문헌고찰과 더불어 보고하는 바이다.
증례
48세 남자환자가 3년전 발생한 무통성의 단단하고 서서히 커지는 우측 뺨의 종물을 주소로 내원하였다. 특이한 기저질환이나 과거력은 없었다.
신체진찰에서 우측 뺨의 적색을 띄는 3cm의 단단한 가동성, 무통성의 종물이 촉지되었다(Fig. 1).
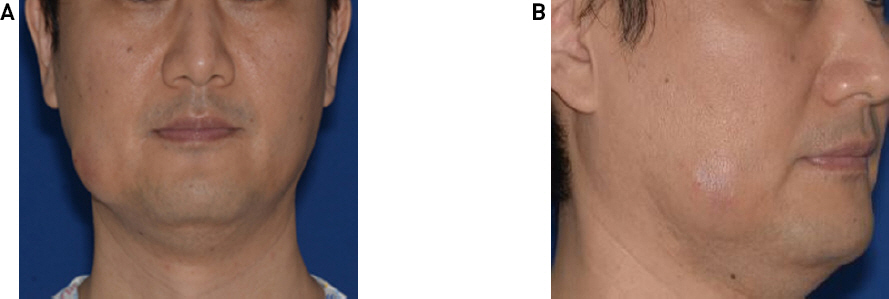
Physical examinations. About 3cm hard, and movable mass was palpated on right cheek with overlying skin erythema.
감별진단을 위해 우선 경부 전산화 단층 촬영을 시행하였다. 우측 뺨 부위에 2.6cm의 경계가 뚜렷한 피하층의 고체성 종물이 관찰되었고 내부에는 석회화가 동반되어 있었다(Fig. 2). 세침흡인검사 상 모기질종 의증(suspicious for pilomatricoma)으로 확인되었다.
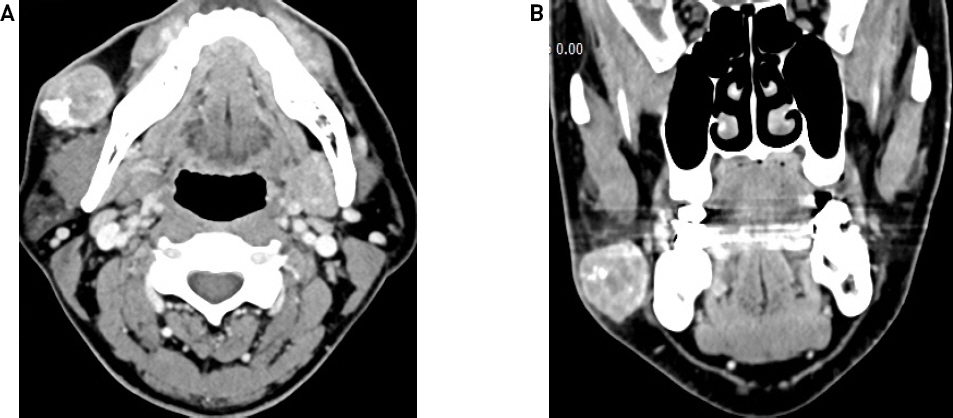
Radiologic findings. CT scan reveals about 2.3 x 2.6 x 2.4 cm sized well defined heterogeneously enhancing high density soft tissue mass at subcutaneous layer of right cheek. The mass had internal calcification and accompanied by peritumoral fat infiltration and skin thickening.
전신마취 하 우측 협부 점막에 약 3cm의 횡절개를 가하였다(Fig. 3A,B). 협부 지방 조직을 박리하여 종물을 확인하였고, 종물이 손상되지 않게 주의하며 박리를 진행하였다. 수술 중 안면신경의 변연 하악분지는 종물에 비해 다소 하부에 위치하여 노출되지 않았다. 종물은 피부와 유착되어 있었으나 메스를 이용하여 피부 천공 없이 완전 절제하였다. 제거 직후 종물에 천공이 되며 keratin 양 물질이 일부 배출되었다(Fig. 3C). 종괴를 절제후 생리식염수를 이용하여 수술부위를 세척하고 4-0 vicryl을 이용하여 배액관 없이 일차 봉합하였다. 이후 환자는 술후 1병일째 합병증 없이 퇴원하였으며, 술 후 1주 후 내원하여 외래에서 발사하였다. 안면부 피부에서는 육안적 이상이 보이지 않았으며, 안면부 감각저하나 안면신경 마비는 관찰되지 않았다. 술 후 2주까지 혈종이나 감염 소견 없이 구강 절개창도 잘 치유 되어 추적관찰을 종료하였다.
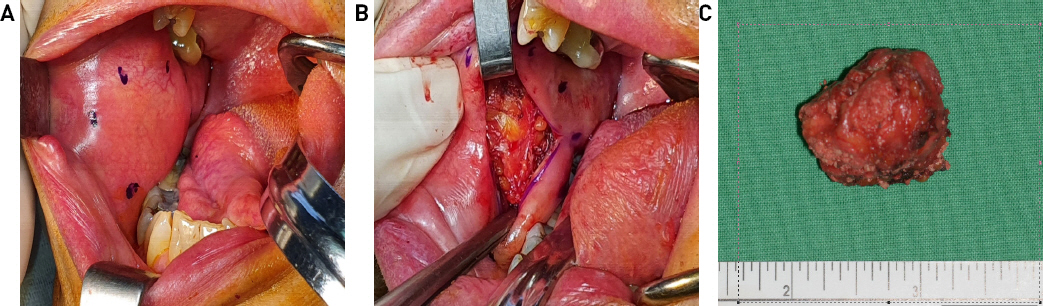
Operative findings. About 2.3 x 2.6 x 2.4 cm sized mass was observed within the right buccal fat(A, B). About 2.5cm, round, and reddish mass was removed(C).
조직검사 상 keratin 양의 석회화된 성분을 포함한 낭성 종물이 관찰되었다. 보다 확대된 시야에서 호염기성 세포질을 포함하고 세포 내 큰 핵과 다양한 크기의 핵소체를 가진 기저양 세포(basaloid cell)의 군집과 호산성의 세포질과 중심부의 핵이 염색되지 않는 무핵성의 유령세포(ghost cell)가 관찰되었으며, 그 사이에 기저양세포가 유령세포로 이행되는 과정에서 핵은 남아있고 세포질이 호산구성으로 염색되는 이행성 세포들이 관찰되었다(Fig. 4).
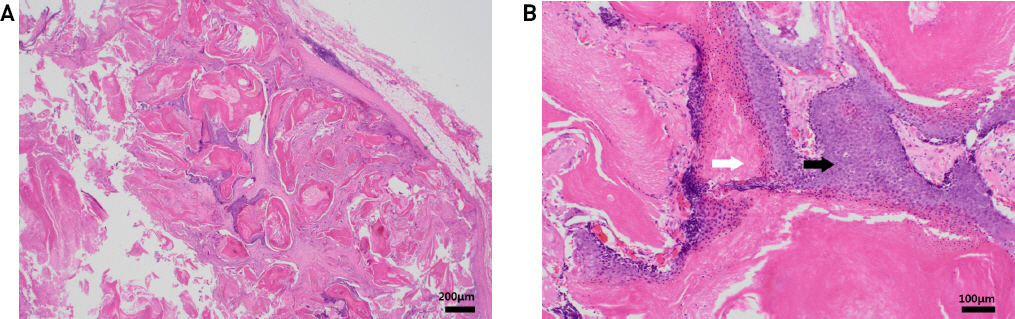
Pathologic findings. Hematoxilin-Eosin stain showed a cystic mass containing keratin squame(HE x40)(A). High power view showed typical basaloid tumor cells having basophilic cytoplasm and regular round nuclei with a prominent nucleoli and eosinophilic anucleated “ghost” cells(Black arrow : basaloid cells. White arrow : ghost cells)(HE x100)(B).
고찰
모기질종은 모낭 기질에서 기원하는 드문 양성 종양으로 주로 두경부영역에 발병하나 신체 어느 부위에서나 발병할 수 있다.6,7) 대개는 약 1cm내외의 가동성의 피부와 유착된 단단한 피하 종물로 발견되며, 덮고 있는 피부는 대개 정상이나 종양과 유착되어 적색이나 푸른색, 암적색 등으로도 보일 수 있다고 보고된다.2,3,8) 대부분 단발성이나 2~3.5%에서 다발성으로 발생할 수 있고, 이런 경우 근긴장성 이영양증, 가아드너 증후군, 터너 증후군, 유육종증, 스테이너트병 등과 연관되어 있다고 보고되고 있다.9,10) 매우 천천히 자라고 드물지만 염증과 동반되어 있거나 흰색 또는 회색의 석회화가 관찰되기도 한다.2,11) 모기질종은 임상적으로 진단하기 어렵고 다른 피부 종양과 혼동될 수 있으며, 세침흡인 검사 시 악성 종양과 유사한 소견을 보일 수 있어 오진되는 경우도 있는 것으로 알려져 있다.3,12) 따라서 피하 낭종, 피지선 낭종, 혈관종, 골종, 침샘기원의 종양과 같은 양성 뿐만 아니라 기저세포암종, 편평세포암종, 림프절에 전이한 암종 등 악성 종양과도 감별이 중요하다.9,12)
영상 진단은 반드시 필요하지는 않으나 악성화가 의심되거나 크기가 클 때, 또는 침범 정도를 파악하거나 이하선 주위에 존재할 때 도움이 되며, 주로 전산화 단층촬영이나 초음파 등을 시행한다.13) 전산화 단층촬영 상 피하 지방층에 위치하고 아래의 근육층으로는 침윤하지 않는 양상의 석회화를 동반한 종물의 형태로 보일 수 있다.11,14) 세침 흡인 검사 상 다양한 크기의 핵과 핵소체를 가진 호염기성 기저양 세포와 그 주변으로 칼슘 축척, 유령세포를 확인하면 진단할 수 있으나 기저양세포만이 관찰되는 경우가 많고, 높은 세포밀도, 바탕에 존재하는 이상 각화성 편평상피세포와 괴사성 배경소견 등으로 악성 종양으로도 오진되기도 하여 주의가 필요하다.12,15)
모기질종의 치료는 수술적 완전 절제가 필요하며, 피부에 단단히 유착되어 있어, 덮고 있는 피부도 일부 같이 절제할 수도 있으며 악성 변이 가능성이 있는 경우 주변 조직을 포함한 광범위 절제가 필요하다.2,3,10,12)
본 증례에서 종양은 피부와 유착된 단단한 양상을 보였고 덮고 있는 피부는 약간의 적색을 띄었다. 그러나 일반적인 모기질종과는 달리 크기는 3cm정도로 다소 크고 발병 위치는 우측 뺨이었다. 소타액선종양 등과의 감별진단이 필요하여 전산화 단층 촬영을 시행하였으며, 2.6cm의 석회화가 동반된 경계가 뚜렷한 피하층의 고체성 종물로 관찰되었고 세침흡인검사를 통해 모기질종을 의심할 수 있었다.
일반적으로 피부절개를 통한 종물의 절제가 필요하지만 안면부 흉터를 피하기 위해 구강내 접근을 시행하였으며, 비록 피부와 유착이 있었지만 메스를 이용하여 피부 천공 없이 절제할 수 있었다.
본 증례는 통상적인 경우와 달리 모기질종이 안면부에 발생하여 일반적인 피부절개를 통한 수술을 했을 경우 큰 흉터를 남길 수 있었지만 구강 접근을 통해 피부절개 없이 완전 절제한 드문 증례로 향후 유사한 증례에 적용될 수 있을 것으로 기대되어 문헌 고찰과 함께 보고하는 바이다.