초음파에서 단순 심경부 감염증으로 오인하여 흡인치료를 시도한 내경정맥 혈전정맥염 (레미에르 증후군) 1례
A Case of Lemierre’s Syndrome, Misdiagnosed as a Simple Deep Neck Infection on Initial Ultrasonography Followed by an Abscess Aspiration Trial
Article information
Trans Abstract
Lemierre’s syndrome is rare disease characterized by anaerobic sepsis, internal jugular vein thrombosis, septic emboli that resulted from head and neck infection. Lemierre’s syndrome has significant morbidity, so immediate, accurate diagnosis and treatment is needed. It is necessary to perform contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CT) for diagnosis. Systemic antibiotics is recommended, and surgical interventions, anticoagulation may beis considered for treatment. We report misdiagnosed case as a simple deep neck infection on initial ultrasonography with simultaneous abscess aspiration but finally diagnosed and treated internal jugular vein thrombophlebitis (Lemierre’s syndrome) on CT scan.
We report a case of a 45-year-old patient, who was diagnosed with a simple deep neck infection and treated with simultaneous abscess aspiration, but finally diagnosed and treated internal jugular vein thrombophlebitis (Lemierre’s syndrome) on CT scan.
서론
레미에르 증후군(Lemierre’s syndrome)은 급성 구인두감염 이후 발생하는 100만명 중 1명으로 발병률이 매우 낮으나 치명적인 질병이다[1,2]. 주로 Fusobacterium necrophorum에 의해 발생하는 내경정맥(Internal jugular vein)의 패혈성 혈전(Septic embolism)이나 패혈증(Sepsis)을 일으키며 패혈성 폐색전증(Septic pulmonary embolism)이나 전이성 농양(Metastatic abscess)으로 이어질 수 있다[3]. 항생제가 발달하기 전에는 레미에르 증후군은 흔하게 발생하는 질병이었으며, 발병 후 급격히 악화되어 치사율이 90%에 이르렀으나 항생제가 발전해감에 따라 발생률이 급격히 감소하였다[4]. 레미에르 증후군의 예후에는 질병의 조기발견 및 치료가 가장 중요하며 치료시기가 늦어질 경우 폐색전증(Pumonary embolism), 골수염(Osteomyelitis) 등을 초래하여 치명적인 결과를 가져올 수 있다[2,5]. 저자들은 최근에 특별한 병력이 없는 45세 남자 환자에게서 초음파로 위중한 양상을 보이지 않는 심부경부감염증을 진단 후 이와 동시에 농양 흡인치료를 시행하였으나, 경부 전산화 단층 촬영에서 내경정맥에 발생한 혈전정맥염(Thrombophlebitis)을 경험하였기에 문헌 고찰과 함께 보고하는 바이다.
증례
45세 남자환자로 2주간 지속되는 좌측 목에 통증. 부종 주소로 내원하였다. 환자는 발열, 오한 있었으나 인후통, 호흡곤란 등 다른 증상 호소하지 않았다. 신체 진찰 상에서 좌측 경부 Level II 구역에서 Level III 구역에 걸친 부종 관찰되었으며 통증과 압통 확인되었다. 경도의 구인두부 발적 소견 보였으며 후두 내시경 상 인후두 내에 부종 보이지 않았다. 체온 37.7℃ 측정되었으며 그 외에 다른 신체검사 상 이상소견은 관찰되지 않았다. 인후두 및 상기도 폐쇄를 유발하지 않는 경도의 경부심부 감염증 임상 진단하에 외래에서 우선 시행한 경부 초음파 검사에서 좌측 경부 Level II-III 구역에 걸친 경계가 불분명한 저음영의 병변이 관찰되었다(Fig. 1). 이에 초음파 세침흡인 검사 시행하였으며 탁한 농양성분이 확인되고, 도플러 검사에서 농양 내 혈관구조는 확인되지 않아 동시에 18 Gauze주사기로 농양 흡인을 최대한으로 재 시행하였으나 탁한 성분으로 인해 거의 흡인되지 않았다. 좌측 병변에서 병리검사 상 화농성 염증 확인되었으며 세균 배양 검사에서 음성 소견, 동시에 시행한 결핵균 핵산증폭검사(Tuberculosis polymerase chain reaction)에서는 음성 확인하였다.
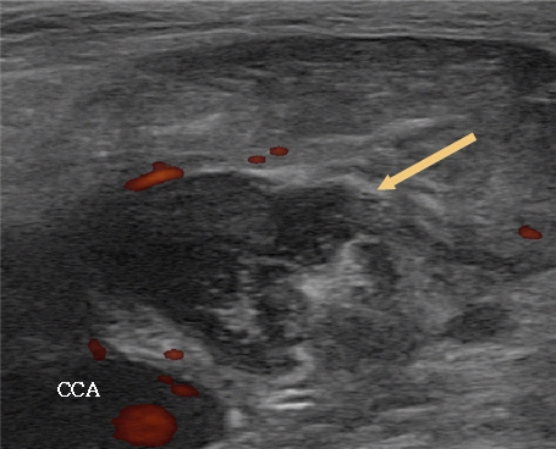
The ultrasonography of the neck obtained on initial hospitalization shows ill-defined hypoechoic, heterogeneous lesions (Arrow) at left neck level 2, suggestive of thrombophlebitis in the internal jugular vein and there is no blood flow in the internal jugular vein. (CCA : Common carotid artery)
입원하여 처음 시행한 말초 혈액 검사 상 백혈구 13,100/μl(중성구 9940/μl), 적혈구 침강 속도 79mm/hr, C-reactive protein 67.12mg/L 소견 보였으며 이는 전신적 염증반응으로 보였다.
흉부 X-선 촬영에서 양측 폐 상엽에서 염증반응의 소견 보였으며 심전도 및 복부 X-선 촬영에서는 이상소견 보이지 않았다. 경부 전산화 단층 촬영에서는 좌측 경동맥 구역(Carotid space)에서 지방 침윤과 함께 불규칙한 모양의 병변이 관찰되었다. 좌측 경동맥의 직접 침윤은 관찰되지 않았으나 좌측 내경정맥과 연결된 혈전으로 보이는 음영결손과 함께 주변으로 연조직 부종, 지방침윤 관찰되었으며 원형의 가장자리가 조영 증가되는 농양이 관찰되었다. 또한 좌측 목빗근에 광범위한 부종 및 좌측 경부 Level II, III, IV, V 구역 림프절 부종 관찰되었다(Fig. 2).
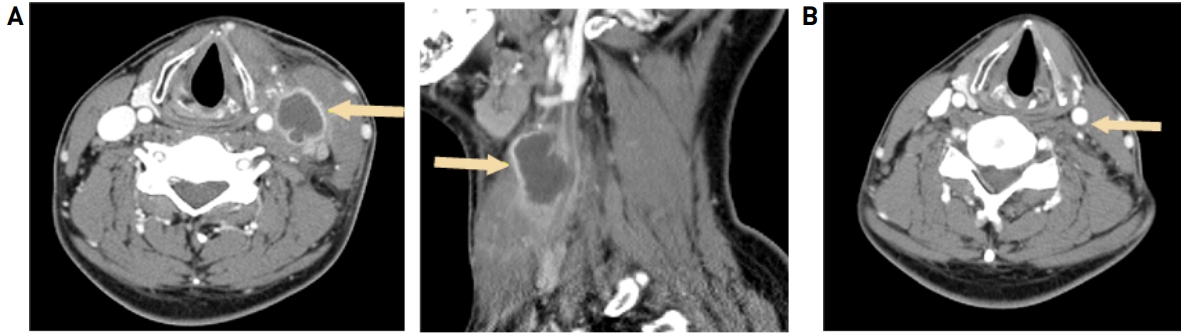
(A) The contrast-enhanced neck computed tomography scan (left; axial image, right; sagittal image at left neck level 2) obtained on admission day showed left internal jugular vein thrombus (Arrow). Filling defect in left jugular vein adjacent to the lesion. (B) Follow up contrast-enhanced neck computed tomography scan obtained on 3 months later showed improved peripheral enhancing central low density mass in left carotid space, and chronic thrombosis and occlusion in left jugular vein (Arrow).
입원 후 정맥을 통한 Ceftriaxone 2g 및 Metronidazole 500mg을 2주간 투약 계획하였다. 입원 후 원인균 감별 위하여 시행한 객담 세균 배양 및 항산균 검사 결과 상음성 소견 보였다. 레미에르 증후군에서 가장 흔하게 발생 가능한 폐 침범을 확인하기 위하여 흉부 고해상도 전산화 단층촬영(High-resolution computed tomography) 시행하였으며 검사 상 양측 폐 상엽에서 결핵 흔적으로 보이는 석회화 및 선형의 불투명한 병변 확인되었으나 패혈성 폐색전증(Septic pulmonary embolism), 폐농양(Lung abscess) 소견은 관찰되지 않았다.
입원 5일째 좌측 경부 Level II 구역에서 Level III 구역에 걸친 부종은 관찰되었으나 말초 혈액 검사 상 백혈구 5,220/μl, 적혈구 침강 속도 54mm/hr, C-reactive protein 4.54mg/L 으로 전신적 염증반응이 호전되는 소견 관찰되었으며 입원 6일째 Cefdinir 100mg, Metronidazole 500mg으로 경구약 변경 및 외래 추적 관찰하였다.
퇴원 1개월 후 좌측 경부 부종 호전되었으며 퇴원 3개월 후 시행한 경부 전산화 단층 촬영에서 좌측 내경정맥 내부의 혈전 및 폐색 여전히 관찰되고 있으나 좌측 경동맥 구역에서 보였던 불규칙한 모양의 염증소견 호전되었음을 확인하였으며 합병증 없이 외래 추적관찰 중이다.
고찰
레미에르 증후군(Lemierre’s syndrome)은 1936년 레미에르에 의해 기술된 질환으로 Fusobacterium necrophorum에 의해 발생한 급성 구인두염(Oropharyngeal infection) 등의 두경부 감염 이후 내경정맥(Internal jugular vein)의 패혈성 혈전 정맥염(Septic thrombophlebitis) 및 패혈성 색전증(Septic embolism)을 일으키는 질환이다[1]. 레미에르 증후군은 발병률은 Denmark에서의 연구에 따르면 100만명 중 1명으로 매우 낮으며 모든 연령층에서 발생가능하나 73.4%가 16-25세의 젊고 이전에 건강하였던 환자에서 나타나며 여성에 비해 남성에서 호발하는 것으로 알려져 있다[2,6].
Chirinos의 연구에 의하면 109개의 사례 중 F. necrophorum이 레미에르 증후군 환자의 배양검사에서 81.7%이며 발견되었으며 12.8%에서 본 증례와 같이 균이 동정되지 않았다. 그 밖에 다른 fusobacterium sp., Bacteroides sp., Peptostreptococcus, group B and C Streptococcus 이 배양되거나 복합감염도 배양되기도 하였다[3].
레미에르 증후군의 진단에서 내경정맥의 혈전정맥염(Thrombophlebitis)을 확인하기 위해 영상의학적 검사는 필수적이다. 경부 전산화 단층촬영은 가장 유용한 검사이며 내경정맥의 확장, 혈관 벽의 조영증가 및 내부 조영 감소를 확인할 수 있다. 자기공명장치 검사 상에서는 조금 더 정확한 정맥조영을 확인할 수 있다[7]. 경부 초음파 검사는 전산화 단층촬영, 자기공명장치에 비해 쉽고 적은 비용으로 내경정맥의 혈전을 확인할 수 있다. 경부 초음파 검사에서는 확장된 내경정맥 내의 저음영 병변이 보이며 고형 성분과 낭성 성분이 복합적으로 보이는 종괴가 관찰된다. 그러나 쇄골, 아래턱 주변부를 관찰하기에 제한이 있으며 저음영의 혈전이 보이지 않을 수 있어 단독 검사로는 충분하지 않다[7,8]. 본 증례는 초음파에서 경계가 불분명한 저음영의 병변이 관찰되었으며 단순 경부 감염증으로 판단되어 직접 초음파 유도하 농양 흡인술을 시행하였고 합병증이 없었으나, 본 증례처럼 posterior acoustic enhancement 가 없는 경정맥 주변의 농양 흡인을 시행할 때 경정맥 강내 잘못된 흡인의 위험성에 대한 주의를 요한다.
레미에르 증후군의 패혈증으로 발전하는 기간은 대체로 1주이다[8]. 합병증이 가장 호발하는 부위는 폐이며 레미에르 증후군의 79%-100% 에서 폐 침범이 일어난다. 폐침범의 경우 폐농양(Lung abscess), 폐색전증(Pulmonary embolism), 호흡부전(Respiratory failure)의 형태로 나타나게 된다. 다음으로 호발하는 부위는 패혈성 관절염(Septic arthritis), 골수염(Osteomyelitis)의 형태로 나타나는 골격계이다. 레미에르 증후군의 13%-27%가량에서 발생하며 고관절, 어깨관절, 무릎관절에서 자주 발생한다. 그 외에도 간농양(Liver abscess), 비장농양(Splenic abscess), 신장농양(Renal abscess) 등의 여러가지 합병증도 보고되고 있다[2].
레미에르 증후군의 치료는 혐기성 균에 효과적인 정맥 항생제를 지속적으로 사용하는 것이다[9]. 가장 흔한 균인 F. necrophorum은 일반적으로 Penicillin, Clindamycin, Metronidazole, Chloramphenicol에 효과가 있으며, Cephalosporin, Erythromycin 그리고 Tetracyclines에서는 다양한 효과가 나타난다. 일부의 F. necrophorum 에서는 β-Lactamase 생성하여 Penicillin에 효과가 없을 수 있으므로 β-Lactamase에 저항성이 있는 항생제(Ticarcillin-clavulanate, Ampicillin-sulbactam, etc)가 권장된다[8]. 항생제 치료하며 지속적으로 패혈증(Sepsis), 전이성 감염(Metastatic abscess), 혈전(Thrombus)의 확산 등의 합병증에 대한 감시가 필수적이며 화농성 고름은 배농이 필요하다. 레미에르 증후군에서 항응고 치료는 대부분의 환자가 항생제 치료만으로 호전되므로 효과에 대해 아직 정립된 바가 없다[10]. 몇몇 연구에서 항생제 치료 이후 패혈성 혈전이 지속되는 경우 시도해볼 수 있으며 내경정맥의 혈전이 해면정맥동(Cavernous sinus)으로 전파되는 임상양상이 보일 경우 사용해볼 수 있다고 하고 있다[8]. 수술적인 치료는 경부 농양이나 편도주위 농양, 인후두 농양 등이 있을 경우 배농하기 위하여 필요하다. 항생제 사용 이전에는 패혈성 색전증을 막기 위해 내경정맥 결찰술 혹은 절제술을 시행하였으나 최근에는 충분한 항생제 치료에도 불구하고 패혈성 혈전증이 지속되는 경우 고려해볼 수 있다[3]. 본 증례의 환자는 입원하여 정맥을 통해 Ceftriaxone 및 Metronidazole을 투여한 후 정맥혈전 호전된 것을 확인 후 퇴원예정이었으나 환자의 거절로 외래 통해 치료 지속하기로 하여 경구 투약으로 2주간 항생제 치료를 지속하였으며 이후 합병증 발생하지 않아 2차적인 수술적인 치료, 항응고 치료는 진행하지 않았다.
결론
저자들은 우선 시행한 초음파에서 단순 심경부 감염증으로 오인한 증례를 경부 전산화 단층 촬영에서 내경정맥혈전증으로 확인 후 적절한 항생제 치료를 시행하였으며 이에 합병증 없이 좋은 결과를 얻어 문헌고찰과 함께 보고하는 바이다. 레미에르 증후군은 경부 초음파 검사상 저음영의 병변이나 낭성의 종괴로 보이기 때문에 심경부 감염증과 유사하게 보일 수 있어 주의를 요한다. 본 증례는 경계가 불분명한 저음영의 병변에서 세침흡인검사를 시행하였으나 내경정맥의 손상 및 출혈 가능성 있어 세침흡인검사 및 농양 흡인술은 신중하게 시행되었어야 하며 정확한 진단을 위하여 추가 영상검사가 필요하였다. 레미에르 증후군은 발병률이 낮고 익숙한 질환이 아니기 때문에 진단이 쉽지 않을 수 있다. 그러나 레미에르 증후군은 패혈성 혈전으로 인한 합병증으로 생명을 위협할 수 있는 질환이기 때문에 적절한 진단 및 치료가 필요하며 경부 통증, 부종이 있을 경우 항상 의심해보는 것이 중요하다.